CC 01: Map Reduce

Intro
map 과 reduce 라는 단어는 functional language 에서 왔다.
- map: processes each record sequentially and independently
- reduce: processes set of all records in batches
(map square '(1 2 3 4))
;; (1 4 9 16)
(reduce + '(1 4 9 16))
;; (+16 (+9 (+4 1)))
;; 30
MapReduce

(http://webmapreduce.sourceforge.net/)
Map: Parallelly process a large number of individual records to generate intermediate key/value pairs
Reduce: processes and merges all intermediate values associated per key
각 키는 하나의 reducer 에 할당되고, partitioning keys 에 의해 reduce 가 진행된다. 자주 쓰이는 기법으로 hash partitioning 이 있다. hash(key) % # of reduce servers
public static class MapClass extends MapReduceBase
implements Mapper<LongWriteable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throws IOException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
output.collect(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class ReduceClass extends MapReduceBase
implements Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output,
Reporter reporter) throw IOException {
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
public void run(String inputPath, String outputPath) throw Exception {
// The job
JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCount.class);
conf.setJobName("mywordcount");
// The keys are words
(srings) conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// The values are counts (ints)
conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
conf.setMapperClass(MapClass.class);
conf.setReducerClass(ReduceClass.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPat(conf, new Path(inputPath);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path(outputPath));
JobClient.runJob(conf);
}
MapReduce Application
(1) Distributed Grep
- input: large set of files
- output: lines that match pattern
- map: emits a line if it matches the supplied pattern
- reduce: copies the intermediate data to output
(2) Reverse Web-Link Graph
- input: web graph(tuple
(a,b)where pagea-> pageb) - output: for each page, list of pages that link to it
- map: process we log and for each input
<source, target>, it outputs<target, source> - reduce: emits
<target, list(source)>
(3) Count of URL Access Frequency
- input: log of accessed URLs
output: for each URL, the number of total accesses for that URL
map: process web log and outputs
<URL, 1>multiple reducers: emits `
chain another MapReduce job to calculate
overall_count
(4) Sort
- map task’s output is sorted (e.g., quicksort)
- reduce task’s input is osrted (e.g., mergesort)
따라서 정렬을 하기 위해
- map:
<key, value>-><value, _>(identity) - reduce:
<key, value>-><key, value>(identity)
이 때 parttition key 로 range 를 사용하는 것이 가능하다. 다만, 특정 구간에 data 가 몰려있을 수 있으므로 dstiribution 을 고려해 reducer 에게 할당해주면 된다.
Scheduling
일반 user 는
- Write a Map program, write a Reduce program
- Submit job; wait for result
- Need to know nothing about parallel/distributed programming
그러나 내부적으로는
- Parallelize Map
- Transfer data from Map to Reduce
- Parallelize Reduce
- Implement Stroage for Map input, Map output, Reduce input, Reduce output
그리고 reduce 가 시작되기 전에 반드시 map 이 끝나야 한다. 다시 말해서 map phase 와 reduce phase 사이에는 barrier 가 있어야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 결과가 부정확할 수 있다.
이제 하나하나씩 살펴보자.
(1) Parallelize Map: Easy. Each map task is independent of the other
(2) Transfer data from Map to Reduce: All map output records with same key assigned to same Reduce task. Use Partitionning Function
(3) Parallelize Reduce: Easy. Each reduce task is independent of the other
(4) Implement Storage for Map input, Map output, Reduce input and Reduce output:
- Map input: from distributed file system
- Map output: to local disk at Map node; Use local file systems
- Reduce input: from (multiple) remote disks; Uses local file systems
- Reduce output: to distributed file system
DFS 의 예로 Google File System, HDFS 등이 있다.
하둡은 스케쥴러로 *YARN, Yet Another Resouce Negotiator*를 사용한다. YARN 은 각 서버를 a collection of containers 로 취급한다. 여기서 container = some CPU + some Memory 다.
YARN 은 크게 3파트로 나눌 수 있는데
- Global Resource Manager(RM): scheduling
- Per-server Node Manager(NM): Daemon and server-specific functions
- Per-application(job) Application Master(AM): Container negotiation with RM and NMs, Detecting task failures of that job
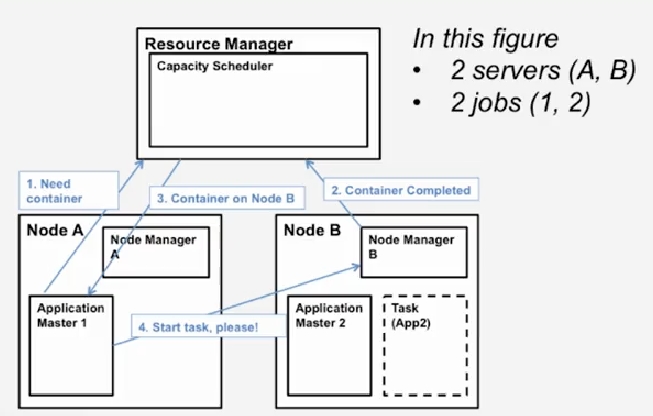
container 가 필요하면 AM1 이 RM 에게 알리고, Node B 의 NM2 에서 Task 가 끝나면, RM 이 Node A 의 AM1 에게 사용 가능한 컨테이너가 있다는 사실을 알려 AM1 이 NM2 에게 컨테이너를 사용하겠다는 요청을 보내는 식이다.
Fault-Tolerance
(1) Server Failure
- NM hearbeats to RM. If server fails RM lets all affected AMs know, and AMs take action
- NM keeps track of each task running at its server. If task fails while in-progress, mark the task as idle and restart it
- AM heartbeats to RM. On failure, RM restarts AM, which then syncs up with its running tasks
(2) RM Failure
- Use old checkpoints and bring up secondary RM
- Heartbeats also used to piggyback container requests. Avoids extra mesages
요약하자면, NM, AM 은 RM 에게 heartbeat 를 보낸다. NM 에서 오류가 나면 RM 이 영향을 받는 AM 에게 알리고, 해당 AM 이 적절히 처리한다. 또한 NM 은 task 를 유지하면서, task 에러가 발생하면 재시작한다. AM 에서 오류가 나면 RM 이 재시작하고, 해당 AM 의 태스크와 싱크를 맞춘다. RM 에서 오류가 날 경우엔 secondary RM 을 이용한다.
Stragglers
slow nodes 를 부르는 다른말이다. speculative execution 으로 해결할 수 있다. 보통 느린 이유는 disk, network bandwidth, CPU, memory 등 때문인데 task 를 복제해서 다른 node 에서 돌린 뒤 먼저 완료되는 노드의 결과를 이용하는 방식이다.
Perform backup (replicated) execution of straggler task: task considered done when first replica completed
Locality
cloud 의 hierarchical topology 때문에 GFS, HDFS 등은 각 chunk 를 3군데에 복제한다. 이때 같은 rack 에 위치할수도 아닐수도 있다.
MapReduce 연산에서는 map task 를 스케쥴링할때 가능하면 다음의 순서로 배치한다.
(1) chunk 가 있는 머신에 or failing that
(2) 아니면 같은 rack 에 or failing that
(3) Anywhere
Summary
(1) MapReduce uses parallelization + aggregation to schedule applications across clusters.
(2) Need to deal with failure
(3) Plenty of ongoing research work in scheduling and fault-tolerance for Mapreduce and Hadoop
Refs
(1) Title Image
(2) Cloud Computing Concept 1 by Indranil Gupta, Coursera
(3) MapReduce Image
comments powered by Disqus