Posted in Angular, Trend Factory, factory, service, provider, injector
Angular, Providers
Comment

자그마한 프로젝트를 엇그제 시작했습니다. 오늘 해야 할 일은 Linkedin, Github API 를 붙이는 일인데, 그 전에 Angular 를 좀 보고 넘어가겠습니다. 아래는 angular-fullstack 으로 만들면 생성되는 템플릿 코드인데, 어디서 부터 시작해야할지 감이 안잡히네요!
angular.module('app', [
'ngCookies',
'ngResource',
'ngSanitize',
'ui.router',
'ui.bootstrap'
])
.config(function ($stateProvider, $urlRouterProvider, $locationProvider, $httpProvider) {
$urlRouterProvider
.otherwise('/');
$locationProvider.html5Mode(true);
$httpProvider.interceptors.push('authInterceptor');
})
.factory('authInterceptor', function ($rootScope, $q, $cookieStore, $location) {
return {
// Add authorization token to headers
request: function (config) {
config.headers = config.headers || {};
if ($cookieStore.get('token')) {
config.headers.Authorization = 'Bearer ' + $cookieStore.get('token');
}
return config;
},
// Intercept 401s and redirect you to login
responseError: function(response) {
if(response.status === 401) {
$location.path('/login');
// remove any stale tokens
$cookieStore.remove('token');
return $q.reject(response);
}
else {
return $q.reject(response);
}
}
};
})
.run(function ($rootScope, $location, Auth) {
// Redirect to login if route requires auth and you're not logged in
$rootScope.$on('$stateChangeStart', function (event, next) {
Auth.isLoggedInAsync(function(loggedIn) {
if (next.authenticate && !loggedIn) {
$location.path('/login');
}
});
});
});
config, run
원문은 Angular Document: Module Loading & Dependencies
configuration 과 run block 은 bootstrap 과정에서 실행되는데
- configuration block 에서는 provider, constant 만 injected 될 수 있고
- run block 은 injector 가 생성되고, 어플리케이션을 구동하기 위해 사용된 후에 실행됩니다. instance 와 constant 만 injected 될 수 있습니다.
angular.module('myModule', []).
config(function(injectable) { // provider-injector
// you can only inject Providers (not instances)
// into config block
}).
run(function(injectable) { // instance-injector
// you can only inject instances (not Providers)
// into run blocks
});
아래는 동일한 코드를 다른 메소드를 이용해 작성한 애플리케이션 초기화 코드입니다.
angular.module('myModule', []).
value('a', 123).
factory('a', function() { return 123; }).
directive('directiveName', ...).
filter('filterName', ...);
// is same as
angular.module('myModule', []).
config(function($provide, $compileProvider, $filterProvider) {
$provide.value('a', 123);
$provide.factory('a', function() { retrun 123; });
$compileProvider.directive('directiveName', ...);
$filterProvider.register('filterName', ...);
});
배운것보다 모르는게 더 많이 생겼습니다. Provider, $provide, injectable 이 뭘까요?
Providers
원문은 Angular Document: Providers
angular app 에서 쓰이는 오브젝트들은 intector service 에 의해서 인스턴스화(instantiated) 됩니다. injector 는 두 타입의 오브젝트를 만드는데,
(1) Services: are objects whose API is defined by the developer writing the service
(2) Specialized objects: conform to a specific angular framework API. These objects are one of controllers, directives, filters or animations
injector 가 이러한 서비스를 만들기 위해서는 recipe 를 알려줘야 하는데, 크게 5가지 recipe 가 있습니다.
가장 유명한건 Provider 입니다. 그 외에 Provider 를 이용해 만든 Value, Factory, Service, Constant 가 있습니다.
angular module 은 하나 이상의 Provider 를 포함할 수 있습니다. 애플리케이션이 시작될때 Angular 는 injector 의 새로운 인스턴스를 만들고, ng 모듈, 애플리케이션 모듈, 그리고 그 dependencies 에 있는 모든 recipe 를 하나의 레지스트리에 등록합니다. 그리고 이후에 필요할때마다 injector 는 이 레지스트리에 새로운 인스턴스를 만들어야 할지, 아니면 존재하는 것을 사용할지 질의합니다.
Value recipe 를 이용한 간단한 예제 를 보겠습니다.
var myApp = angular.module('myApp', []).
value('clientId', 'a12345654321x');
myApp.controller('myController', ['clientId',
function(clientId) {
this.clientId = clientId;
}]);
myApp 모듈에 정의되어 있는 clientId Value recipe 를 등록하고 컨트롤러에서 사용했습니다.
Factory
myApp.factory('apiToken', ['clientId', function apiTokenFactory(clientId) {
var encrypt = function(data1, data2) {
// encryption algorithm:
return (data + ':' + data2).toUpperCase();
};
var secret = window.localStorage.getItem('myApp.secret');
var apiToken = encrypt(clientId, secret);
return apiToken;
}]);
Factory recipe 를 이용해서 apiToken 서비스를 정의했습니다. 이 서비스는 Value recipe 를 이용해 만든 clientId 서비스에 의존합니다.
Service
apiToken 서비스를 이용하는 다른 서비스를 Service recipe 를 이용해서 만들어 볼텐데, 동시에 Service recipe 가 어떤 역할을 하는지 비교하기 위해 Factory recipe 로도 만들어 보겠습니다.
function UnicornLauncher(apiToken) {
this.launchedCount = 0;
this.launch = function() {
// Make a request to the remote API and include the apiToken
...
this.launchedCount++;
}
}
myApp.factory('unicornLauncher', ["apiToken", function(apiToken) {
return new UnicornLauncher(apiToken);
}]);
// is same as
myApp.service('unicornLauncher', ["apiToken", UnicornLauncher]);
Factory recipe 로도 만들 수 있지만, 일반적으로 Service recipe 는 new 와 함께 호출되는 서비스를 정의하기 위해 사용합니다. Stackoverflow: Factory vs Service 에서도 그 답변을 찾을 수 있습니다.
예를 들어서 위에서 우리가 정의한 unicornLauncher 서비스는, UnicornLauncher 생성자를 new 로 호출됩니다.
아래는 대략적인 두 함수의 구성입니다.
function factory(name, factoryFn) {
return provider(name, { $get: factoryFn });
}
function service(name, constructor) {
return factory(name, ['$injector', function($injector) {
return $injector.instantiate(constructor);
}]);
}
$injector 는 provider 에 의해 정의된 인스턴스를 angular app 내에서 조회하고, 생성할 수 있습니다. 이외에도 메소드를 호출하거나, 모듈을 로드할 수 있습니다.
Provider
Provider recipe 는 Service 나 Factory 등 다른 recipe 를 구성하는 코어 컴포넌트입니다. 문법적으로는 $get 을 구현한 커스텀 타입입니다. 이 $get 메소드는 Factory recipe 에서 사용했던 것과 같은 factory function 입니다.
다시 말해서, Factory recipe 만들때 하는 일은 empty Provider 에 $get 을 이용해 정의된 factory function 을 가져오는 일입니다.
Provider recipe 는 반드시 애플리케이션이 시작 되기 전에 생성되야 하는 application-wide configuration 을 위한 API 를 정의할때만 사용해야 합니다.
myApp.provider('unicornLauncher', funtion UnicornLauncherProvider() {
var useTinfoilShielding = false;
this.useTinfoilShielding = function(vaue) {
useTinfoilShielding = !!value;
};
this.$get = ["apiToken", function unicornLauncherFactory(apiToken) {
return new UnicornLauncher(apiToken, useTinfoilShielding);
}];
});
myApp.config(["unicornLauncherProvider", function(unicornLauncherProvider) {
unicornLauncherProvider.useTinfoilShielding(true);
}]);
처음에 configuration block config 를 언급하면서 provider, constant 만 injected 될 수 있다고 말했었는데, 이런 이유에서입니다.
regular instance injector 와는 달리 provider injector 에 의해 실행되는 이런 injection 을 통해 모든 provider 가 인스턴스화 (instantiated) 됩니다.
angular 애플리케이션이 부트스트랩되는 동안, provider 가 구성되고, 생성되는 동안에는 service 에 접근할 수 없습니다. 이는 service 가 아직 생성되지 않았기 때문입니다.
configuration phase 가 지난 후에야 services 가 생성되고, 이 단계를 run phase 라 부릅니다. 이 때문에 run block 에서 instance 와 constant 만 injected 될 수 있다고 위에서 언급한 것입니다.
Special Purpose Objects
앞서 Angular 에서 쓰이는 모든 오브젝트는 intector service $injector 에 의해서 초기화 된다고 했었습니다. 일반적인 서비스 오브젝트와, 특별한 목적을 가진 오브젝트들이 있다고 언급하기도 했지요.
이런 특별한 오브젝트들은 프레임워크를 확장하는 플러그인으로서 Angular 에서 정의한 interface 를 구현해야 하는데, 이 인터페이스는 Controller, Directive, Filter, Animation 입니다.
Controller 오브젝트를 제외하고는 이러한 special object 를 생성하기 위해 injector 는 Factory recipe 를 이용합니다. 따라서 인자로 넣어준 팩토리 함수가 디렉티브를 만들기 위해 호출됩니다.
myApp.directive('myPlanet', ['planetName', function myPlanetDirectiveFactory(planetName) {
// directive definition object
return {
restrict: 'E',
scope: {},
link: function($scope, $element) { $element.text('Planet: ' + planetName); }
}
}]);
Controller
myApp.controller('DemoController', ['clientId', function DemoController(clientId) {
this.clientId = clientId;
}]);
Controller 는 조금 다르게, Factory recipe 를 이용하지 않습니다. 인자로 정의한 constructor function 함수가 모듈과 함께 등록됩니다.
애플리케이션이 DemoController 가 필요할때마다 매번 constructor 를 통해서 인스턴스화(instantiated) 합니다. 일반적인 service 와는 다르게, 컨트롤러는 싱글턴이 아닙니다.
지금까지 배운 내용을 정리하면
- The injector uses recipes to create two type of objects: services and special purpose objects
- There are five recipe types that define how to create objects: Value, Factory, Service, Provide, and Constant
- Factory and Service are the most commonly used recipes. The only differences between them is that the Service recipe works better for objects of a custom type, while the Factory can produce primitives and functions
- The Provider recipe is the core recipe type and all the other ones are just syntactic sugar on it
- Provider is the most complex recipe type. You don't need it unless you are building a reusable piece of code that needs global configuration
- All special purpose objects except for the Controller are defined via Factory recipes
Dependency Injection
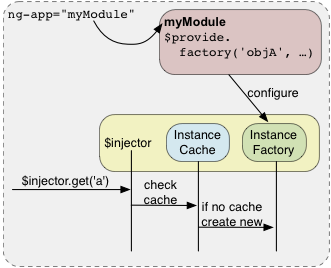
service 는 $injector 에 의해서 싱글턴 인스턴스가 만들어지고, $injector.get() 을 통해 얻을 수 있습니다. 만약 캐시된 인스턴스가 있다면 가져오고 없으면 새로 만듭니다. 아래는 외부에서 injector 를 통해 내부 서비스를 접근하는 방법입니다.
var injector = angular.injector(['myModule', 'ng']);
var greeter = injector.get('greeter');
Refs
(1) [http://galleryhip.com/angular-js-icon.html)
(2) Angular Document
(3) Webdeveasy: AngularJS Q
(4) Webdeveasy: AngularJS Interceptor